What is Overall Equipment Effectiveness?
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) is a performance measure commonly used to monitor successful improvements to a process/area/machine. OEE is designed to indicate how effectively a manufacturing operation is utilised. OEE can at times be a complicated metric to understand as it is derived from three individual calculated components. The components of OEE are : Availability, Performance, and Quality.
To calculate an OEE for a single machine first you need to know your Availability, Performance and Quality.
OEE= (AxPxQ)
• A = Represents the percentage of scheduled time that the operation is available to operate. Often referred to as Uptime.
• P= The speed at which the machine runs as a percentage of its designed speed.
• Q= : The Good Units produced as a percentage of the Total Units Started.
How to calculated the components Availability, Performance, and Quality.
Availability is a measurement of Uptime.
Calculation: A = Available Time / Scheduled Time
Performance – is a measurement of speed
Calculation: P= (Parts Produced * Ideal Cycle Time) / Available Time
Quality – measures the Good Units produced as a percentage of the Total Units Started.
Calculation: Q = Good Units / Units Started
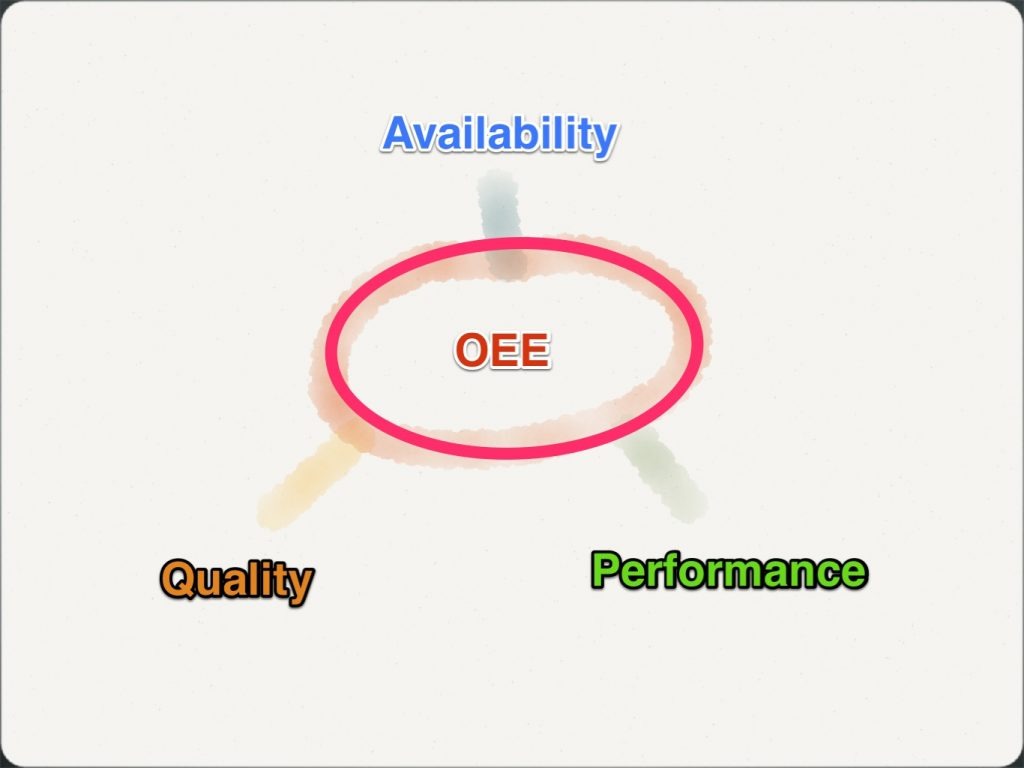
Here is a working example on how to calculate Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) for a single machine example. First you need to know your production data in order to calculate the inputs for 1) Availability, 2) Performance and 3) Quality elements. These include:
- Hours per shift
- Total break
- Machine downtime
- Planned run rate
- Total units manufactured
- Reject or rework pieces
1) Machine Availability
The Availability is the measurement of the time the machine was able to performance its function.
Calculation: Availability = Available Time / Scheduled Time
Example:
The CNC Lathe is scheduled to run for an 8 hour shift.
The normal shift includes total of 45 minute meal breaks.
During the shift the Machine experiences 60 minutes of unscheduled downtime.
Scheduled Time = 8hrs – 0.75hrs break = 7.25hrs
Available Time = 7.25hrs Scheduled – 1 hours Unscheduled Downtime = 6.25 hrs
Machine Availability = 6.25hrs/ 7.25 Scheduled = 86%
2) Performance
The Performance Metric is a measurement of speed that machine needs to run in order to performance its function.
Calculation: Performance = (Total units Manufactured * PLanned Run Rate) / Available Time
Example:
Available Time = 6.25 hrs
The Planned Rate for the part being produced is 40 Units/Hour or 250 part per shift
The Machine produced 242 Total Units during the shift.
Time to Produce Parts = 242 Units for the shift
Performance = 242 / 250 parts = 97%
3) Quality
The Quality metric measures the Good Units produced as a percentage of the Total Units produced.
Calculation: Quality = Good Units / Total Units produced
Example:
242 Units were manufactured in order to produce the 230 Good Units.
Quality = 230 Good Units / 242 total units manufactured = 95.0%
These percentages can now be entered into the standard formula for OEE.
OEE= (AxPxQ)
OEE= (86% x 97% x 95%)
OEE= 79%
This calculation can be performed easily with spreadsheet template for daily measure to be added to a team’s production board.