When applying Lean manufacturing principles, in order to improve we have to start with understanding the current manufacturing landscape.
Typically an organisation will have lots of raw data stored in computer programs and reports that can be difficult to work with. Understanding raw data is a key step in taking action towards improvement, so how do we do that.
There are a good number of analytical techniques to use sometimes a simple flowchart or a box load of control charts is needed to bring people together in order to solve a problem.
Each problem is different and which techniques to use may vary from situation to situation. However from a lean view using analytical tools to solve problems is 80% about developing leaders to learn to think differently and 20% on solving the problem. A better leader will solve more problems.
Below are some analytical tools that you can use to gain insights to understand current issues.
Lean tip – Analytical techniques don’t apply themselves and too much analysis leads to paralysis.
Input/Output Analysis
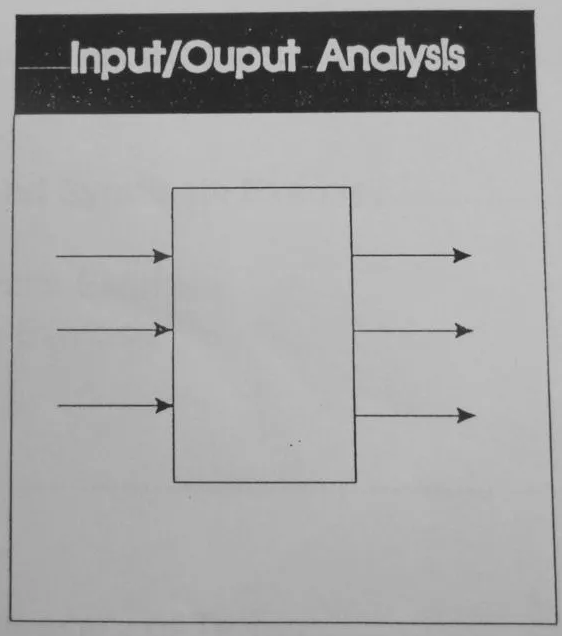
The Lean tip here is not to describe the sequence of activities required generate the outputs from the inputs. Treat the process a a black box and focus only on the all inputs and all outputs of a process step.
Flowcharting
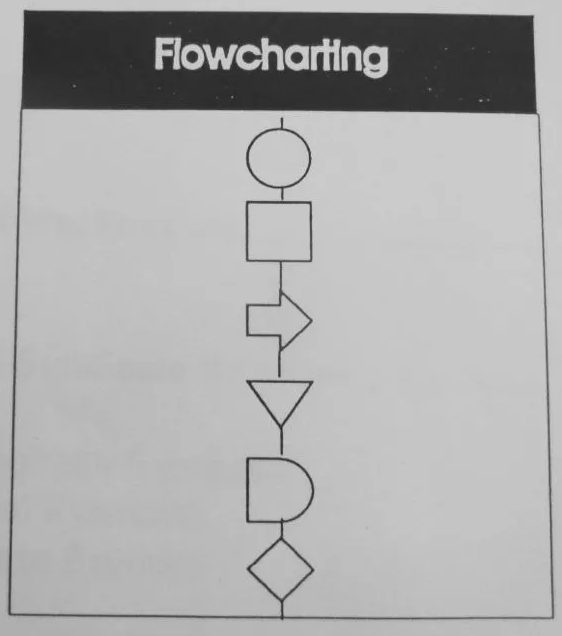
The two most common types of boxes in a flowchart are a circle for a process step, and a diamond as a decision step. Flowcharts are useful in lean manufacturing as we can clearly separate the value adding operations from the Non-value adding operations.
Pareto Rule
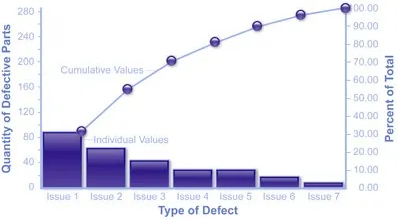
- 80% of your complaints come from 20% of your customers
- 80% of your sales come from 20% of your products
- 80% of your quality errors are made by 20% of your processes
Therefore, many businesses have use this rule to improve profitability by focusing on the most effective areas and ignoring the rest, of the problems until a later time.
Fishbone (Cause and Effect)

It provides a process to clearly define the “Effect” and then puts you to thinking about the possible causes, based on the categories of common problems in manufacturing.
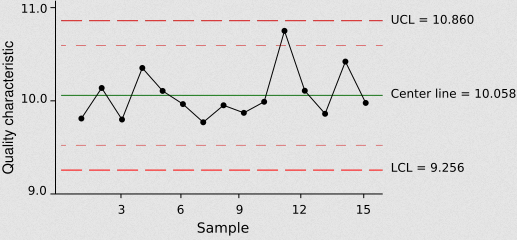
Control Charts